Product Description
SINOTRUK CZPT Truck Gearbox Assy Used on Hw19710, Hw15710 Spareworks
| Company | ChinaMach Industry Co.,Ltd |
| Brand | SINOTRUK HOWO/WEICHAI/MAN/SHACMAN/FAW/FOTON/AUMAN/NORTHBENZ/SHXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.I/ |
| QUALITY | Original part/OE part |
| Payment term | T/T L/C , Flexible billing method |
| Packing | Standard packing |
We can provide:
TRUCK
Sales Chinese trucks and construction machinery,Provide modificationsu,pgrades, consulting services
SPARE TRUCK
Supply China Truck spare parts and construction machinery parts. Products Include: Sinotruk HOWO, CZPT Power , Fonton, Shacman, SHXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.I, DOOXIN
SERVICE
Provide cargo warehousing, packaging, shipping and export agency services
Agent procurement, inspection The inspection agency
| Application: | Machinery, Heavy Duty Truck |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Speed Changing |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Manual |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
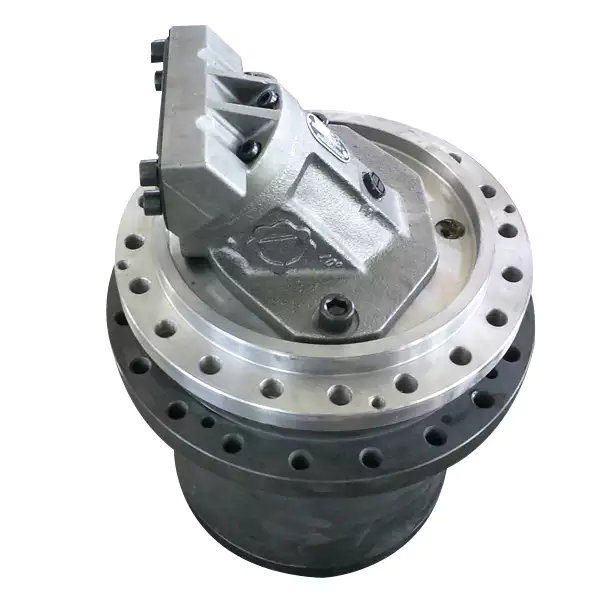

Concept of Coaxial and Parallel Shaft Arrangements in Planetary Gearboxes
Coaxial and parallel shaft arrangements refer to the orientation of the input and output shafts in a planetary gearbox:
- Coaxial Shaft Arrangement: In this arrangement, the input and output shafts are aligned along the same axis, with one shaft passing through the center of the other. This design results in a compact and space-efficient gearbox, making it suitable for applications with limited space. Coaxial planetary gearboxes are commonly used in scenarios where the gearbox needs to be integrated into a compact housing or enclosure.
- Parallel Shaft Arrangement: In a parallel shaft arrangement, the input and output shafts are positioned parallel to each other but not on the same axis. Instead, they are offset from each other. This configuration allows for greater flexibility in designing the layout of the gearbox and the surrounding machinery. Parallel shaft planetary gearboxes are often used in applications where the spatial arrangement requires the input and output shafts to be positioned in different locations.
The choice between a coaxial and parallel shaft arrangement depends on factors such as available space, mechanical requirements, and the desired layout of the overall system. Coaxial arrangements are advantageous when space is limited, while parallel arrangements offer more design flexibility for accommodating various spatial constraints.

Signs of Wear or Damage in Planetary Gearboxes and Recommended Service
Planetary gearboxes, like any mechanical component, can exhibit signs of wear or damage over time. Recognizing these signs is crucial for timely maintenance to prevent further issues. Here are some common signs of wear or damage in planetary gearboxes:
1. Unusual Noise: Excessive noise, grinding, or whining sounds during operation can indicate worn or misaligned gear teeth. Unusual noise is often a clear indicator that something is wrong within the gearbox.
2. Increased Vibration: Excessive vibration or shaking during operation can result from misalignment, damaged bearings, or worn gears. Vibration can lead to further damage if not addressed promptly.
3. Gear Tooth Wear: Inspect gear teeth for signs of wear, pitting, or chipping. These issues can result from improper lubrication, overload, or other operational factors. Damaged gear teeth can affect the gearbox’s efficiency and performance.
4. Oil Leakage: Leakage of gearbox oil or lubricant can indicate a faulty seal or gasket. Oil leakage not only leads to reduced lubrication but can also cause environmental contamination and further damage to the gearbox components.
5. Temperature Increase: A significant rise in operating temperature can suggest increased friction due to wear or inadequate lubrication. Monitoring temperature changes can help identify potential issues early.
6. Reduced Efficiency: If you notice a decrease in performance, such as decreased torque output or inconsistent speed, it could indicate internal damage to the gearbox components.
7. Abnormal Gear Ratios: If the output speed or torque does not match the expected gear ratio, it could be due to gear wear, misalignment, or other issues affecting the gear engagement.
8. Frequent Maintenance Intervals: If you find that you need to service the gearbox more frequently than usual, it could be a sign that the gearbox is experiencing excessive wear or damage.
When to Service: If any of the above signs are observed, it’s important to address them promptly. Regular maintenance checks are also recommended to detect potential issues early and prevent more significant problems. Scheduled maintenance should include inspections, lubrication checks, and replacement of worn or damaged components.
It’s advisable to consult the gearbox manufacturer’s guidelines for recommended service intervals and practices. Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of the planetary gearbox and ensure it continues to operate efficiently and reliably.

Challenges and Solutions for Managing Power Transmission Efficiency in Planetary Gearboxes
Managing power transmission efficiency in planetary gearboxes is crucial to ensure optimal performance and minimize energy losses. Several challenges and solutions are involved in maintaining high efficiency:
1. Gear Meshing Efficiency: The interaction between gears can lead to energy losses due to friction and meshing misalignment. To address this, manufacturers use precision manufacturing techniques to ensure accurate gear meshing and reduce friction. High-quality materials and surface treatments are also employed to minimize wear and friction.
2. Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential to reduce friction and wear between gear surfaces. Using high-quality lubricants with the appropriate viscosity and additives can enhance power transmission efficiency. Regular maintenance and monitoring of lubrication levels are vital to prevent efficiency losses.
3. Bearing Efficiency: Bearings support the rotating elements of the gearbox and can contribute to energy losses if not properly designed or maintained. Choosing high-quality bearings and ensuring proper alignment and lubrication can mitigate efficiency losses in this area.
4. Bearing Preload: Incorrect bearing preload can lead to increased friction and efficiency losses. Precision assembly and proper adjustment of bearing preload are necessary to optimize power transmission efficiency.
5. Mechanical Losses: Various mechanical losses, such as windage and churning losses, can occur in planetary gearboxes. Designing gearboxes with streamlined shapes and efficient ventilation systems can reduce these losses and enhance overall efficiency.
6. Material Selection: Choosing appropriate materials with high strength and minimal wear characteristics is essential for reducing power losses due to material deformation and wear. Advanced materials and surface coatings can be employed to enhance efficiency.
7. Noise and Vibration: Excessive noise and vibration can indicate energy losses in the form of mechanical inefficiencies. Proper design and precise manufacturing techniques can help minimize noise and vibration, indicating better power transmission efficiency.
8. Efficiency Monitoring: Regular efficiency monitoring through testing and analysis allows engineers to identify potential issues and optimize gearbox performance. This proactive approach ensures that any efficiency losses are promptly addressed.
By addressing these challenges through careful design, material selection, manufacturing techniques, lubrication, and maintenance, engineers can manage power transmission efficiency in planetary gearboxes and achieve high-performance power transmission systems.


editor by CX 2023-11-29
China Best Sales New CZPT CZPT Truck Parts Transmission Gearbox Assy Hw13710 Hw15710 near me supplier
Product Description
new CZPT CZPT truck components Transmission gearbox assy HW13710 HW15710
technical specs:
reference photographs:
suggested spare parts listing:
Spare areas reference pictures:
Our warehouse:
About our organization:
| Part No. | HW13710; HW15710 |
| EN part name | Sinotruk Transmission, HOWO Gearbox |
| Size:cm | 140x75x80cm |
| Weight:kg | 400KG |
###
| Pos | Number of part | Quantity | Standard sepcification | Designation |
| 1 | 61557010008 | 1 | Gearcase | |
| 2 | VG2600010830 | 1 | Air compressor gear cover | |
| 3 | VG14010040 | 1 | Gasket | |
| 4 | VG2600010928 | 1 | Front oil seal carrier | |
| 5 | VG1047010038 | 1 | Front oil seal | |
| 6 | VG1500010008A | 1 | Camshaft gear cover | |
| 7 | VG14010070 | 1 | Gasket | |
| 8 | 190003813429 | 14 | M8×22-8.8-ZN DIN939 | Stud |
| 9 | 190003932023 | 17 | B8-ZN DIN137 | Wave spring washer |
| 10 | 190003900085 | 4 | Q5281220 | Spring type Straight pin |
| 11 | 190003802576 | 1 | M10×90-8.8-ZN DIN933 | Hex head bolt |
| 12 | 190003932024 | 1 | B10-ZN DIN137 | Wave spring washer |
| 13 | 190003800571 | 1 | M10×80-8.8-ZN DIN931 | Hex head bolt |
| 14 | 190003931122 | 10 | B10-ZN DIN127 | Spring lockwasher |
| 15 | 190011260039 | 6 | M6×30-8.8-H.Y GB/T5782 | Hex head bolt |
| 16 | 190003862524 | 2 | M10×20-8.8-ZN DIN912 | Socket cap screw |
| 17 | 190003932025 | 2 | A10-ZN DIN137 | Saddle shaped spring washer |
| 18 | 190003871252 | 17 | M8-8-ZN DIN934M | Hexagon nut |
| 19 | 190003813443 | 1 | M8×30-8.8-ZN DIN939 | Stud |
| 20 | 190003962051 | 1 | CM30×1.5-5.8 DIN7604 | Screw plug |
| 21 | 190003901507 | 4 | 10m6×16 DIN7 | Straight pin |
| 22 | 190003802523 | 3 | M10×25-8.8-ZNDIN933 | Hex head bolt |
| 23 | 190011620016 | 2 | M12×45-8.8-ZN GB/T898 | Stud |
| 190003813638 | M12×35-8.8-ZN DIN939 | Stud | ||
| 24 | 190003813628 | 6 | M12×30-8.8-ZN DIN939 | Stud |
| 25 | 190003888453 | 8 | VM12-8-ZN DIN980 | Self-locking nut |
| 26 | 190003813467 | 2 | Q1200865F3 | Stud |
| 27 | VG9003080001 | 6 | Sealing washer | |
| 28 | VG2600010934 | 1 | Front oil seal carrier gasket | |
| 29 | 190003930271 | 2 | A10.5-ST DIN125 | Flat washer |
| 30 | 190003802561 | 6 | M10×75-8.8-ZN DIN933 | Hex head bolt |
| Part No. | HW13710; HW15710 |
| EN part name | Sinotruk Transmission, HOWO Gearbox |
| Size:cm | 140x75x80cm |
| Weight:kg | 400KG |
###
| Pos | Number of part | Quantity | Standard sepcification | Designation |
| 1 | 61557010008 | 1 | Gearcase | |
| 2 | VG2600010830 | 1 | Air compressor gear cover | |
| 3 | VG14010040 | 1 | Gasket | |
| 4 | VG2600010928 | 1 | Front oil seal carrier | |
| 5 | VG1047010038 | 1 | Front oil seal | |
| 6 | VG1500010008A | 1 | Camshaft gear cover | |
| 7 | VG14010070 | 1 | Gasket | |
| 8 | 190003813429 | 14 | M8×22-8.8-ZN DIN939 | Stud |
| 9 | 190003932023 | 17 | B8-ZN DIN137 | Wave spring washer |
| 10 | 190003900085 | 4 | Q5281220 | Spring type Straight pin |
| 11 | 190003802576 | 1 | M10×90-8.8-ZN DIN933 | Hex head bolt |
| 12 | 190003932024 | 1 | B10-ZN DIN137 | Wave spring washer |
| 13 | 190003800571 | 1 | M10×80-8.8-ZN DIN931 | Hex head bolt |
| 14 | 190003931122 | 10 | B10-ZN DIN127 | Spring lockwasher |
| 15 | 190011260039 | 6 | M6×30-8.8-H.Y GB/T5782 | Hex head bolt |
| 16 | 190003862524 | 2 | M10×20-8.8-ZN DIN912 | Socket cap screw |
| 17 | 190003932025 | 2 | A10-ZN DIN137 | Saddle shaped spring washer |
| 18 | 190003871252 | 17 | M8-8-ZN DIN934M | Hexagon nut |
| 19 | 190003813443 | 1 | M8×30-8.8-ZN DIN939 | Stud |
| 20 | 190003962051 | 1 | CM30×1.5-5.8 DIN7604 | Screw plug |
| 21 | 190003901507 | 4 | 10m6×16 DIN7 | Straight pin |
| 22 | 190003802523 | 3 | M10×25-8.8-ZNDIN933 | Hex head bolt |
| 23 | 190011620016 | 2 | M12×45-8.8-ZN GB/T898 | Stud |
| 190003813638 | M12×35-8.8-ZN DIN939 | Stud | ||
| 24 | 190003813628 | 6 | M12×30-8.8-ZN DIN939 | Stud |
| 25 | 190003888453 | 8 | VM12-8-ZN DIN980 | Self-locking nut |
| 26 | 190003813467 | 2 | Q1200865F3 | Stud |
| 27 | VG9003080001 | 6 | Sealing washer | |
| 28 | VG2600010934 | 1 | Front oil seal carrier gasket | |
| 29 | 190003930271 | 2 | A10.5-ST DIN125 | Flat washer |
| 30 | 190003802561 | 6 | M10×75-8.8-ZN DIN933 | Hex head bolt |
The Parts of a Gearbox
There are many parts of a Gearbox, and this article will help you understand its functions and components. Learn about its maintenance and proper care, and you’ll be on your way to repairing your car. The complexity of a Gearbox also makes it easy to make mistakes. Learn about its functions and components so that you’ll be able to make the best choices possible. Read on to learn more. Then, get your car ready for winter!
Components
Gearboxes are fully integrated mechanical components that consist of a series of gears. They also contain shafts, bearings, and a flange to mount a motor. The terms gearhead and gearbox are not often used interchangeably in the motion industry, but they are often synonymous. Gearheads are open gearing assemblies that are installed in a machine frame. Some newer designs, such as battery-powered mobile units, require tighter integration.
The power losses in a gearbox can be divided into no-load and load-dependent losses. The no-load losses originate in the gear pair and the bearings and are proportional to the ratio of shaft speed and torque. The latter is a function of the coefficient of friction and speed. The no-load losses are the most serious, since they represent the largest proportion of the total loss. This is because they increase with speed.
Temperature measurement is another important preventive maintenance practice. The heat generated by the gearbox can damage components. High-temperature oil degrades quickly at high temperatures, which is why the sump oil temperature should be monitored periodically. The maximum temperature for R&O mineral oils is 93degC. However, if the sump oil temperature is more than 200degF, it can cause seal damage, gear and bearing wear, and premature failure of the gearbox.
Regardless of its size, the gearbox is a crucial part of a car’s drivetrain. Whether the car is a sports car, a luxury car, or a farm tractor, the gearbox is an essential component of the vehicle. There are two main types of gearbox: standard and precision. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. The most important consideration when selecting a gearbox is the torque output.
The main shaft and the clutch shaft are the two major components of a gearbox. The main shaft runs at engine speed and the countershaft may be at a lower speed. In addition to the main shaft, the clutch shaft has a bearing. The gear ratio determines the amount of torque that can be transferred between the countershaft and the main shaft. The drive shaft also has another name: the propeller shaft.
The gears, shafts, and hub/shaft connection are designed according to endurance design standards. Depending on the application, each component must be able to withstand the normal stresses that the system will experience. Oftentimes, the minimum speed range is ten to twenty m/s. However, this range can differ between different transmissions. Generally, the gears and shafts in a gearbox should have an endurance limit that is less than that limit.
The bearings in a gearbox are considered wear parts. While they should be replaced when they wear down, they can be kept in service much longer than their intended L10 life. Using predictive maintenance, manufacturers can determine when to replace the bearing before it damages the gears and other components. For a gearbox to function properly, it must have all the components listed above. And the clutch, which enables the transmission of torque, is considered the most important component.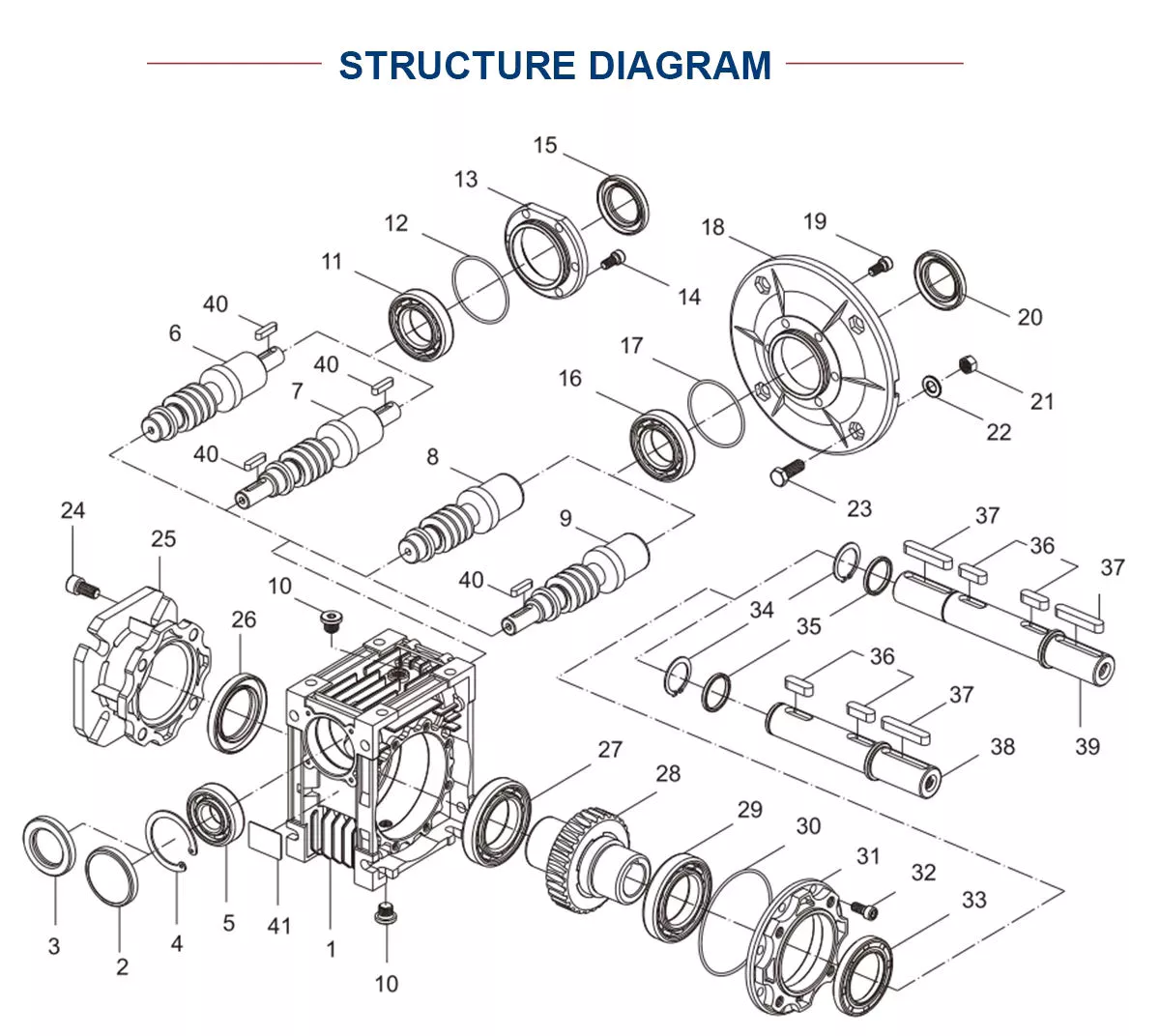
Functions
A gearbox is a fully integrated mechanical component that consists of mating gears. It is enclosed in a housing that houses the shafts, bearings, and flange for motor mounting. The purpose of a gearbox is to increase torque and change the speed of an engine by connecting the two rotating shafts together. A gearbox is generally made up of multiple gears that are linked together using couplings, belts, chains, or hollow shaft connections. When power and torque are held constant, speed and torque are inversely proportional. The speed of a gearbox is determined by the ratio of the gears that are engaged to transmit power.
The gear ratios in a gearbox are the number of steps a motor can take to convert torque into horsepower. The amount of torque required at the wheels depends on the operating conditions. A vehicle needs more torque than its peak torque when it is moving from a standstill. Therefore, the first gear ratio is used to increase torque and move the vehicle forward. To move up a gradient, more torque is required. To maintain momentum, the intermediate gear ratio is used.
As metal-to-metal contact is a common cause of gearbox failure, it is essential to monitor the condition of these components closely. The main focus of the proactive series of tests is abnormal wear and contamination, while the preventative tests focus on oil condition and additive depletion. The AN and ferrous density tests are exceptions to this rule, but they are used more for detecting abnormal additive depletion. In addition, lubrication is critical to the efficiency of gearboxes.
Maintenance
Daily maintenance is a critical aspect of the life cycle of a gearbox. During maintenance, you must inspect all gearbox connection parts. Any loose or damaged connection part should be tightened immediately. Oil can be tested using an infrared thermometer and particle counters, spectrometric analysis, or ferrography. You should check for excessive wear and tear, cracks, and oil leaks. If any of these components fail, you should replace them as soon as possible.
Proper analysis of failure patterns is a necessary part of any preventative maintenance program. This analysis will help identify the root cause of gearbox failures, as well as plan for future preventative maintenance. By properly planning preventative maintenance, you can avoid the expense and inconvenience of repairing or replacing a gearbox prematurely. You can even outsource gearbox maintenance to a company whose experts are knowledgeable in this field. The results of the analysis will help you create a more effective preventative maintenance program.
It is important to check the condition of the gearbox oil periodically. The oil should be changed according to its temperature and the hours of operation. The temperature is a significant determinant of the frequency of oil changes. Higher temperatures require more frequent changes, and the level of protection from moisture and water reduces by 75%. At elevated temperatures, the oil’s molecular structure breaks down more quickly, inhibiting the formation of a protective film.
Fortunately, the gear industry has developed innovative technologies and services that can help plant operators reduce their downtime and ensure optimal performance from their industrial gears. Here are 10 steps to ensure that your gearbox continues to serve its purpose. When you are preparing for maintenance, always keep in mind the following tips:
Regular vibration analysis is a vital part of gearbox maintenance. Increased vibration signals impending problems. Visually inspect the internal gears for signs of spiraling and pitting. You can use engineers’ blue to check the contact pattern of gear teeth. If there is a misalignment, bearings or housings are worn and need replacement. Also make sure the breathers remain clean. In dirty applications, this is more difficult to do.
Proper lubrication is another key factor in the life of gearboxes. Proper lubrication prevents failure. The oil must be free of foreign materials and have the proper amount of flow. Proper lubricant selection depends on the type of gear, reduction ratio, and input power. In addition to oil level, the lubricant must be regulated for the size and shape of gears. If not, the lubricant should be changed.
Lack of proper lubrication reduces the strength of other gears. Improper maintenance reduces the life of the transmission. Whether the transmission is overloaded or undersized, excessive vibration can damage the gear. If it is not properly lubricated, it can be damaged beyond repair. Then, the need for replacement gears may arise. However, it is not a time to waste a lot of money and time on repairs.

